INTERACTIVE DESIGN Exercises3
GCD 60904 / INTERACTIVE DESIGN
Exercises3
Bachelor of Design (Honours) in Creative Media
LIU CHENG RUI (0370930)
Instructions
Lecture notes
week4
In today's class, Mr. Rahman told us about the WEB language.This includes things like HTML.
Basic concepts of HTML elements:
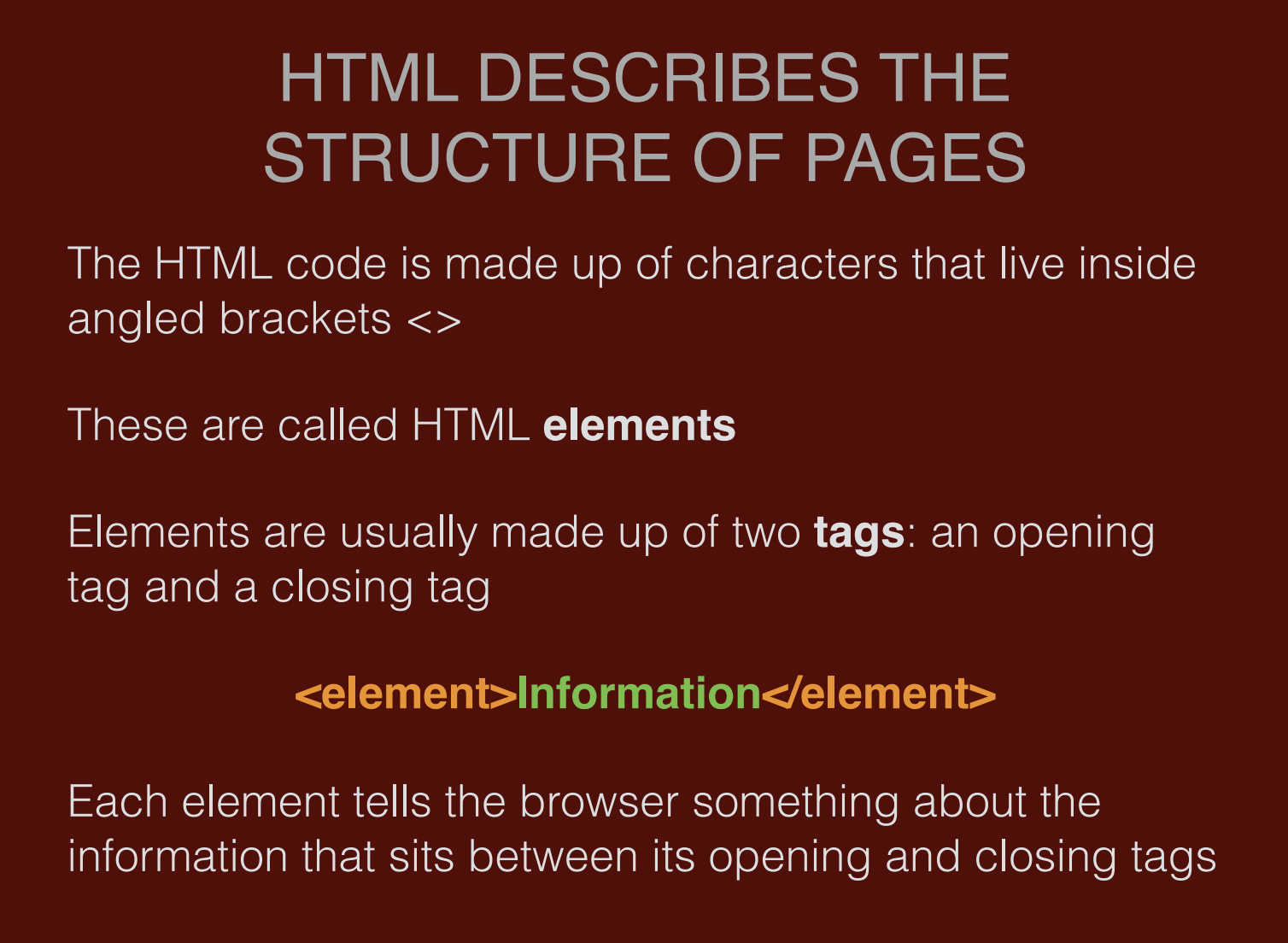
HTML code is made up of characters that are located inside Angle brackets <> and are called HTML elements.
An element is usually made up of two labels, an open label and a closed label.
What HTML tags do:
HTML elements surround information by opening tags <element> and closing tags </element>. Tags tell the browser how to handle and display the content between tags.
The role of information:
The content between elements is information, and each HTML element conveys specific information about that content to the browser.
<body> tag:
The body element contains everything that appears in the main browser window. This is the body of the web page, and all user-visible content is placed in the body tag.
<head> tag:
The head element precedes the body element and contains meta information about the web page. It is usually not displayed directly in the web content, but contains information such as the page title, style sheet links, scripts, and so on.
<title> tag:
The title element is inside the head, and its contents are displayed on a TAB bar at the top of the browser, usually used to identify the title of a web page.
<ol> Tags:
<ol> stands for ordered list and is used to create an ordered list. Each item in the list is automatically numbered, usually in numerical order.
<li> Tags:
<li> stands for list item. The contents of each list item are located between the open label <li> and the closed label </li>. The li tag applies to all list types (including ordered lists <ol> and unordered lists <ul>).
week7
1. Selectors are used to define which elements should receive a particular style, such as color, font, spacing, etc.
2. They are an important part of web development because they give you control over the presentation and layout of the web page.
Universal selector: Used to select all elements on the page. It is indicated by an asterisk (*). Use caution as it affects all elements and can lead to inefficient CSS.
Element selector: The simplest type of selector that locates HTML elements by tag name.
class selector: Used to locate elements with specific class attributes. Multiple elements can share the same class. To select an element with a specific class, use the. Symbol followed by the class name.
Pseudo-class selector: Selects an element based on its state or its position relative to other elements.
Exercises
Week4 EX HTML and CSS Document Development
During the class, Mr. Rahman gave us some knowledge about HTML step by step and showed us how to work on text.
Exercise 3 - Personal CV Page
To design and build a personal CV page using basic HTML and CSS. This exercise will help you organize information into sections, practice styling text, and create a clean, professional-looking page layout.
Production process 1
Personal CV Page Link: Personal resume
Feedback
week4
Through this study, I have a clear understanding of the basic knowledge of HTML, master the basic structure of HTML documents, the use of tags, and how to build lists and other content.
week7
In learning and using CSS selectors, I got the following feedback:
The importance of hierarchy and detail:
The diversity of CSS selectors reflects the precise control of hierarchy and detail in web design.
Balance simplicity with efficiency:
Selectors in CSS need to be used with care, especially universal selectors (*) and descendant selectors (), which, while powerful, can affect performance if left unchecked.
The power of precise control: ID selectors, class selectors, sub-selectors, etc., allow developers to precisely control the elements of the web page, thus achieving highly customized layout and style.

























Comments
Post a Comment